
The Tramex concrete moisture meters are calibrated using gravimetric testing as a baseline.
Gravimetric testing is widely used in the moisture content analysis of sample materials and is considered the most accurate method of determining moisture content percentage. The gravimetric concrete moisture testing method involves weighing a concrete sample before and after it has been dried in an oven. The difference in weight is used to calculate the percentage moisture content present in the concrete sample.
The calibration of Tramex concrete moisture meters is based on the gravimetric testing method for concrete. The readings correspond to the actual moisture content percentage of the concrete material under test. The calibration of the concrete moisture meters can be checked with the calibration check plate to ensure the calibration is correct before conducting a moisture test. If the calibration exceeds the required parameters, the meter should be returned to Tramex for re-calibration.
Below is a field study demonstrating the accuracy of the Tramex concrete moisture meters.
The VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland
The VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland Ltd conducted research on bridge deck concrete for moisture content using various methods and concluded that the Tramex Concrete Moisture Encounter moisture meter — CME, gave results that were best comparable with the Gravimetric testing method, the oven drying method.
In laboratory measurements of the concrete moisture content by the NDT method the Tramex Concrete Moisture Encounter gave results which were best comparable with the results of the oven drying method.
The report finds and confirms that Tramex Concrete Encounter moisture meters are the best NDT method to gather quantitative moisture content on concrete slabs.
The VTT conducted these tests without any requests from Tramex, and Tramex has no ties or relations with VTT.
Here's the link to the report on VTT's website: Concrete moisture measuring methods for bridge construction site. Below is the VTT Report’s Abstract in its original version.
LAUKKANEN, Kyosti: Concrete moisture measurement methods for bridge construction sites. Espoo 2000, VTT COMMUNITIES AND INFRASTRUCTURE, Research report 548.
ABSTRACT
There is a risk of damages to waterproofing, if the moisture level in the bridge deck is too high during the laying works of waterproofing. Conventional methods of moisture measurement on bridge sites of the Finnish National Road Administration — CME comprise drying of concrete samples in oven and measuring of relative humidity in holes drilled into the bridge deck. Both methods are destructive, relatively time-consuming and laborious. In addition, the drilled-hole method is susceptible to errors of measurement in the open air.
The aim of the study was to elucidate the available methods and devices for measuring concrete moisture at bridge deck waterproofing sites. These devices should be easy to use. appropriate for site conditions and they should be alternatives to present methods. The most promising methods were to be tested in the laboratory.
The research method was to measure moisture in several concrete samples of different moisture levels by using several measuring devices. The results were compared with each other and to results of the reference methods. In the study 13 different devices for moisture measurement in concrete were tested using concrete in three different moisture conditions within RH 70 - 95 %. The age of concrete varied between two weeks and 3.5 years.
VTT Communities and Infrastructure and VTT Building Technology, as ordered by the Finnish National Road Administration, carried out the study in the year 2000. The results will be utilized in acquiring measuring devices and in developing specifications for bridge construction.
On the basis of the study it was possible to assort the devices which worked best in laboratory test conditions. Several of the tested devices were not applicable with an adequate accuracy to measurement of high moisture contents of concrete on bridge decks.
In laboratory measurements of the concrete moisture content by the NDT-method the Tramex Concrete Moisture Encounter gave results which were best comparable with the results of the oven drying method.
Among the test methods for moisture measurement based on relative humidity, a Rotronic AWVC device and a test tube method (using a Vaisala sensor) gave in 2-4 weeks old concrete slabs results, which were relatively close to the values measured in holes drilled in concrete.
These test results are valid only in the constant laboratory climate conditions used in the study. At a bridge site many variables (e.g. temperature changes, rain, wind and in old bridges possibly chlorides) will also affect the results. The study should be continued with the three methods thriven well in the laboratory (Tramex Concrete Moisture Encounter, Rotronic AWVC and the test tube method) at real bridge site climate conditions, and the results compared with the methods used currently on those bridges.
Report Graph - Testing Method x Moisture Content %
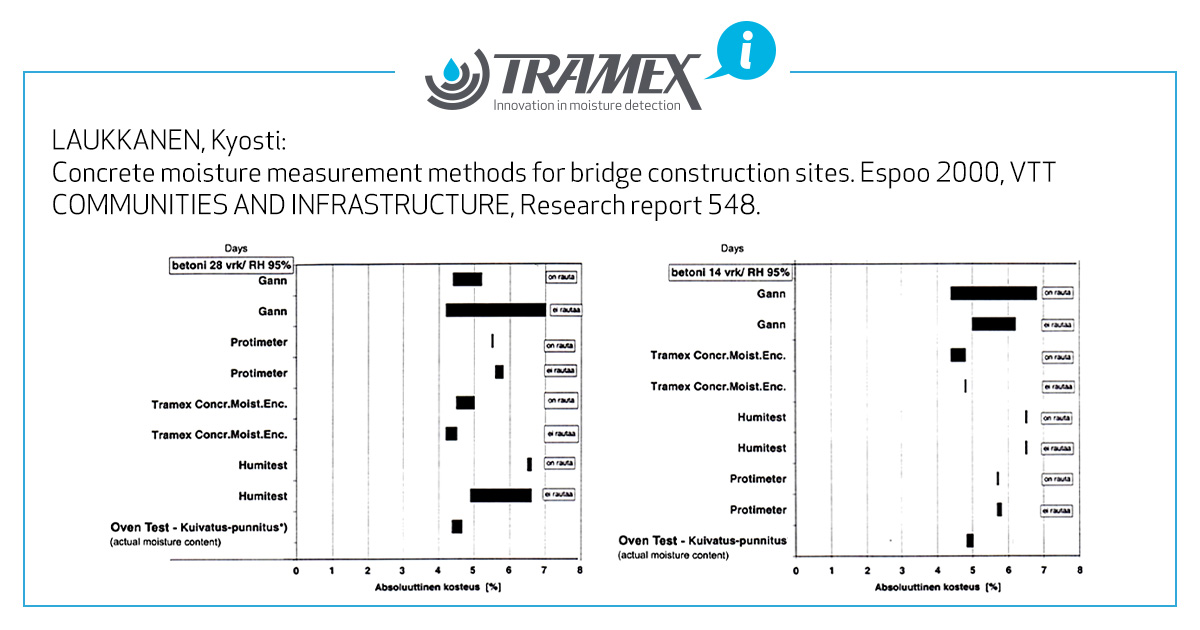
The above graphs show the test results of 4 different Non-Destructive Test methods compared to the Oven Test (Gravimetric Test) on 28-day old concrete (left chart) and 14-day old concrete (right chart). The first listing of each method is on polished concrete and the second is on bare concrete. The width of the black bars on the graph indicates the range of results from multiple tests on the same sample meaning the smaller the bar the more consistent the test method.